Gravitational field
Two masses separated by a distance exert gravitational forces on one another. This is called action at–a–distance. They interact even though they are not in contact. This interaction can also be explained with the field concept. A particle or a body placed at a point modifies a space around it which is called gravitational field. When another particle is brought in this field, it experiences gravitational force of attraction. The gravitational field is defined as the space around a mass in which it can exert gravitational force on other mass.
Gravitational field intensity
Gravitational field intensity or strength at a point is defined as the force experienced by a unit mass placed at that point. It is denoted by E. It is a vector quantity. Its unit is N kg–1.
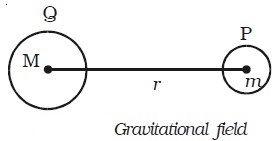
Consider a body of mass M placed at a point Q and another body of mass m placed at P at a distance r from Q.
The mass M develops a field E at P and this field exerts a force F = mE.
The gravitational force of attraction between the masses m and M is F = 2 GM m / r^2
The gravitational field intensity at P is E = f/M
∴ E = GM/r^2
Gravitational field intensity is the measure of gravitational field.
Gravitational potential difference
Gravitational potential difference between two points is defined as the amount of work done in moving unit mass from one point to another point against the gravitational force of attraction.
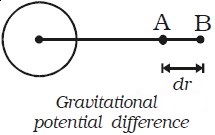
Consider two points A and B separated by a distance dr in the gravitational field. The work done in moving unit mass from A to B is dv = WA → B Gravitational potential difference dv = − E dr Here negative sign indicates that work is done against the gravitational field.
Gravitational potential
Gravitational potential at a point is defined as the amount of work done in moving unit mass from the point to infinity against the gravitational field. It is a scalar quantity. Its unit is N m kg^−1.
Expression for gravitational potential at a point
Consider a body of mass M at the point C. Let P be a point at a distance r from C. To calculate the gravitational potential at P consider two points A and B. The point A, where the unit mass is placed is at a distance x from C.
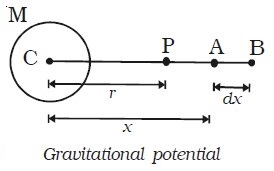

The gravitational potential is negative, since the work is done against the field. (i.e) the gravitational force is always attractive.

