Hydrostatic pressure
Integration of eqn (3) for a homogeneous fluid of constant density gives
p + gρz = const. (4)
The value of the constant in eqn. (4) is determined by the value of p at a point where z is specified. If the fluid is a liquid with a horizontal free surface at which the pressure is atmospheric (pa) this free surface may be taken as the datum level z = 0. For a point at a depth h below the surface, h = −z (since h is measured downwards whereas z is measured upwards) and, from eqn. (4)
p = pa + ρgh (5)
From the formula (5) it is clear that the pressure increases linearly with the depth, whatever the shape of any solid boundaries may be. Equation (5) shows that the pressure at a point in a liquid in equilibrium is due partly to the weight of the liquid. Thus atmospheric pressure is usually effective, even if indirectly, on all surfaces, and over the differences of height normally encountered it is sensibly constant. Consequently it is often simpler to regard atmospheric pressure as the zero of the pressure scale. As we have already mentioned A pressure expressed relative to atmospheric pressure is known as a gauge pressure. The pressure expressed by equation
p = ρgh (6)
is named as the hydrostatic pressure.
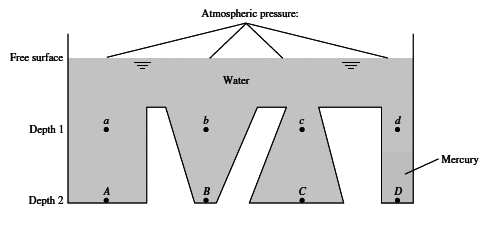
Figure 3: Hydrostatic-pressure distribution. Points a, b, c, and d are at equal depths in water and therefore have identical pressures. Points A, B, and C are also at equal depths in water and have identical pressures higher than a, b, c, and d. Point D has a different pressure from A, B, and C because it is not connected to them by a water path.
The direct proportionality between hydrostatic pressure and h for a fluid of constant density enables the pressure to be simply visualized in terms of the vertical distance h = p/ρg. The quotient p/ρg is termed the pressure head corresponding to p. For a liquid without a free surface, as for example in a closed pipe, p/ρg corresponds to the height above the pipe to which a free surface would rise if a small vertical tube of sufficient length and open to atmosphere known as a piezometer tube were connected to the pipe

