Passive Elements (Loads)
There are 2 types of elements found in electrical circuits: Active and Passive Elements
Passive Elements (Loads)
Passive elements are those elements which are capable of receiving the energy. Some passive elements like inductors and capacitors are capable of storing a finite amount of energy, and return it later to an external element. More specifically, a passive element is defined as one that cannot supply average power that is greater than zero over an infinite time interval. Resistors, capacitors, Inductors fall in this category.
Inductor
A wire of certain length, when twisted into a coil becomes a basic inductor. The symbol for inductor is shown in Fig. (b). If current is made to pass through an inductor, an electromagnetic field is formed. A change in the magnitude of the current changes the electromagnetic field. Increase in current expands the fields, and decrease in current reduces it.
Therefore, a change in current produces change in the electromagnetic field, which induces a voltage across the coil according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. i.e., the voltage across the inductor is directly proportional to the time rate of change of current.
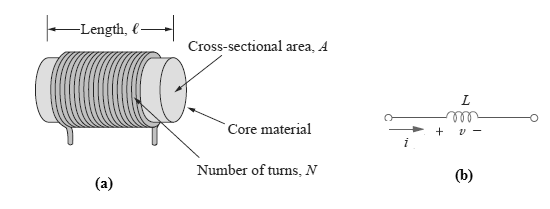
Fig. above – (a) Typical Inductor, (b) Circuit symbol of Inductor
Mathematically,
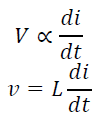
where L is the constant of proportionality called the inductance of an inductor. The unit of inductance is Henry (H) and we can rewrite the above equation as

Integrating both sides from time 0 to t, we get


From the above equation we note that the current in an inductor is dependent upon the integral of the voltage across its terminal and the initial current in the coil
The power absorbed by the inductor is

The energy stored by the inductor is
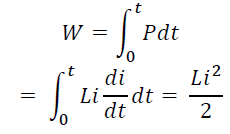
From the above discussion, we can conclude the following.
- The induced voltage across an inductor is zero if the current through it is constant. That means an inductor acts as short circuit to
- A small change in current within zero time through an inductor gives an infinite voltage across the inductor, which is physically impossible. In a fixed inductor the current cannot change abruptly i.e., the inductor opposes the sudden changes in
- The inductor can store finite amount of energy. Even if the voltage across the inductor is zero
- A pure inductor never dissipates energy, only stores it. That is why it is also called a non- dissipative passive element. However, physical inductors dissipate power due to internal resistance.

