Trigonometric formulae
Trigonometric formulae – Basic definitions
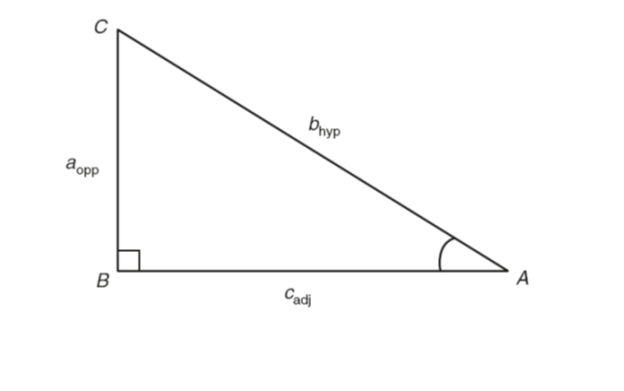
Trigonometric formulae – In the right-angled triangle shown below, a is the side opposite to angle A, b is the hypotenuse of the triangle and c is the side adjacent to angle A. By definition:
SinA=opp/hyp=a/b
cosA=adj/hyp=c/b
tanA=opp/adj=a/c
cosecA=hyp/opp=b/a=1/sinA
secA=hyp/adj=b/c=1/cosA
cotA=adj/opp=c/a=1/tanA
Identities
sin2A+cos2A=1
1 +tan2A= sec2A
1 +cot2A =cosec2A
sin(-A) =-sin A
cos(-A)=cos A
tan(-A)=-tan A
Compound and double angle formulae
sin(A+B)= sinA cos B+cos A sin B
sin(A –B)=sinA cos B-cos A sin B
cos(A+B)=cos A cos B-sinA sin B
cos(A –B) =cos A cos B+sinA sin B
tan(A+B)=(tanA +tan B)/(1-tan A tan B)
tan(A–B)=(tanA -tan B)/(1+tan A tan B)
sin 2A =2 sinA cos A
cos 2A= cos2A -sin2A= 2 cos2A -1=1 -2 sin2A
tan 2A =(2 tan A)/(1-tan2A)
‘Product to sum’ formulae
sinAcosB=1/2[sin(A+B)+sin(A-B)]
cosAsinB=1/2[sin(A+B)-sin(A-B)]
cosAcosB=1/2[cos(A+B)+cos(A-B)]
sinAsinB=-1/2[cos(A+B)-cos(A-B)]
Triangle formulae
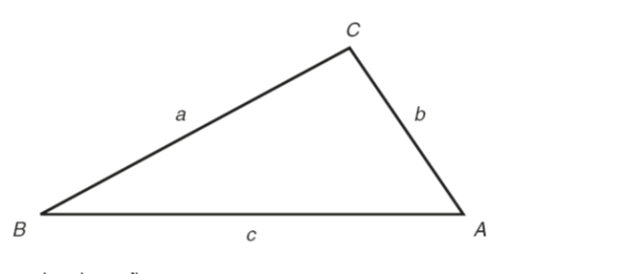
With reference to the above figure:
Sine rule:
a/sinA= b/sin B= c/sin C
Cosine rule:
a2 =b2 +c2 -2bc cos A
b2=c2 +a2 -2ca cos B
c2=a2+b2 -2ab cos C
Area:
Area=1/2ab sin C=1/2 bc sinA =1/2ca sin B
Also
Area=√s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
where: s is the semi-perimeter, that is, (a+b+c)/2

