Work
When a force is applied to a body so that it causes the body to move, the force is said to be doing work. The work done is the product of the distance moved in metres (m) and the applied force in newtons (N) measured in the direction of motion. Therefore the work done is measured in newton metres and the unit of work is joule (J) where 1Nm=1 J. Figure 1(a) shows a body is being moved by a force F along a horizontal plane. Since the force is acting on the body parallel to the horizontal plane, the work done is product of the force F (N) and the distance s (m). If the force is 50 N and the distance is 3 m, then the work done is:
50 N × 3m=150Nm=150 J
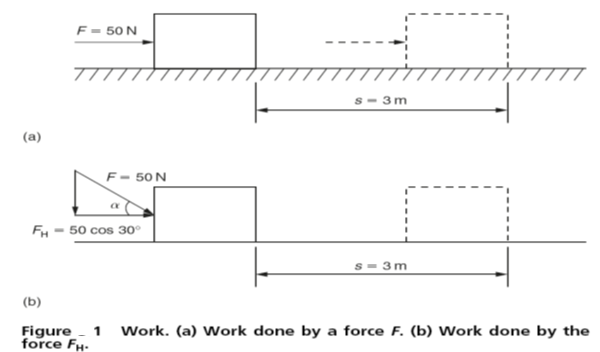
In Fig. 1(b) the force is inclined through the angleα to the direction of motion. In this case the force vector has to be resolved into its vertical and horizontal components as shown. The component force that is parallel to the direction of motion of the body is F cosα. Therefore the work done is s ×F cos α joules. If the force (F) is again 50 N, the distance (s) is again 3 m and the angle α is 30° the work done will be:
W = 3m ×50 N ×0.866=129.9Nm=129.9 J

